Full Body MRI
500+ conditions including cancers of the brain, thyroid, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder, ovaries, uterus, and prostate. Also scans for risk of strokes, risk of aneurysms, abnormal cysts, endometriosis, fatty liver, fibroids, kidney stones, hernias, iron overload, and diverticulitis.

Neurological MRI with Skeletal
Everything in the MRI Scan with Spine. Also scans for signs of neurodegeneration, multiple sclerosis and dementia; adds brain age analysis and body composition assessment (fat and muscle volume); hip evaluation for labrum, cartilage, and joint health; knee evaluation for meniscus, ACL, and MCL injuries.

Cardiac MRI
A low-dose MRI or CT scan to look for lung cancer, pulmonary nodules, emphysema, and more. A Nanox assessment of your CT images to look for heart disease by assessing for artery plaque buildup with a coronary artery calcium (CAC) score.

Aging is a complex biological process influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetic predisposition environmental exposures, and lifestyle choices. At its core, aging stems from the gradual accumulation of molecular and cellular damage over time. This damage manifests in various ways, impacting the structure and function of our cells,tissues, and organs. While hallmarks of aging are inevitable, their impact can be modulated through targeted interventions.
what causes aging
DNA damage

Telomere shortening
Gene expression
errors
Cells don't die when they're supossed to
Stem cell
exhaustion
Imbalanced
metabolism
Proteins
malfunction
The body's energy
machinery malfunctions
Inefficient cell communication
We believe in leveraging the power of cutting-edge science and technology to illuminate the intricate processes of aging and identify innovative solutions to optimize healthspan and potentially extend lifespan.Our approach is rooted in understanding these fundamental mechanisms and developing safe personalized strategies to mitigate their effects, paving the way for a future where aging is synonymous with vitality and well-being.
the honed.life way
Hallmark
Accumulation of genetic mutations over time impairs cell function and increases disease risk.
Access Solutions
CRISPR gene editing, senolytics, DNA repair enhancement.

precision diagnostics
Embark on your journey with honed.life's Precision Diagnostics. We transcend traditional testing by employing cutting-edge technologies like genomic sequencing, comprehensive biomarker panels, and advanced imaging studies. This in-depth analysis unveils your unique health blueprint, identifying potential risks and imbalances at their earliest stages – even before symptoms arise. By understanding your genetic predispositions, metabolic profile, and cellular health, we can craft a truly personalized roadmap for your wellness journey. This proactive approach empowers you to make informed decisions about your health, implement targeted interventions, and optimize your longevity potential.
health optimization
Optimize your health and performance, regardless of your starting point, with honed.life's tailored Health & Performance Optimization program. Leveraging insights from precision diagnostics, we craft personalized health interventions that address your unique needs and goals. Whether you're managing chronic conditions or striving for peak vitality, we'll work with you to optimize nutrition, exercise, stress management, and sleep, ensuring a holistic approach to well-being. Beyond physical health, we recognize the importance of cognitive function and mental health in achieving true longevity. With expert guidance and support, you'll embark on a sustainable and enjoyable path towards enhanced energy, improved focus, and a profound sense of vitality.

longevity & well-being
At this point of your journey, you're ready to embrace a future where aging is synonymous with vitality and purpose. Our longevity & well-being program transcends conventional healthcare, focusing on proactive interventions to extend your healthspan and redefine the aging experience.We leverage cutting-edge therapies like senolytics and NAD+ boosting, alongside personalized lifestyle modifications, to support cellular rejuvenation, optimize hormone balance, and foster a profound sense of well-being. Additionally, we harness the power of pharmacogenomics to tailor medications to your unique genetic profile, ensuring optimal efficacy and minimal side effects. We also explore the potential of regenerative medicine, including stem cell and exosome therapies, to promote tissue repair and rejuvenation.
health is innately human...
so is honed.life
A unique journey, designed to support you in a way that
feels natural and intuitive.

join honed.life
This initial consultation will help us understand your unique needs and tailor a plan specifically for you.
Connect with one of honed.life's professionals to discuss your health goals, concerns, and lifestyle.

embrace lifelong
Guided by the expertise of our seasoned practitioners, you'll enter a personalized path to optimal health and longevity.
We'll track your progress every step of the way, conducting periodic reassessments to fine-tune your plan and ensure you're always moving forward.

craft your plan
Together, we'll optimize your healthspan and empower you to refine your lifestyle for lasting well-being.
Your assessment insights will guide us in creating a targeted plan, incorporating vetted therapies and interventions that address the root causes of aging and chronic disease.
it's about a healthspan system
Our platform connects a comprehensive network of advanced technologies, healthcare experts, and innovative providers, all dedicated to maximizing
healthspan.

Individuals are at the center of the Healthspan System. honed.life empowers them with knowledge, tools, and support to take control of their health journey.
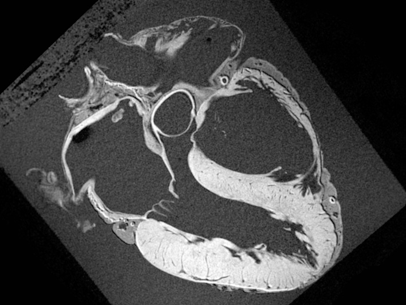
Your heart plays a critical role in your overall health. Get a personalized, clinician-led plan to manage symptoms like high blood pressure, and avoid conditions like diabetes and stroke in the future.
Apolipoprotein B (Apo B)
Apo B helps transport lipids throughout the bloodstream, which is vital for cardiovascular health. Along with other lipid tests, Apo B is a powerful risk marker for cardiovascular disease.
Cholesterol / HDL Ratio
Measures the ratio of total cholesterol levels to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL).
HDL Cholesterol
HDL is part of a comprehensive lipid panel, an essential risk assessment for heart disease. There are two types of cholesterol: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Think of the H as healthy, helpful, heart-supporting cholesterol that helps reduce plaque buildup.
HDL Large
Large HDL particles in the blood are protective; having a higher amount is beneficial because they help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
hs-CRP is revelatory in one's overall health as it relates to the risk of inflammation-related diseases. Chronic inflammation is linked to every major disease: heart disease (even before symptoms occur), type 2 diabetes, cancer, high blood pressure, Alzheimer’s, depression, all autoimmune diseases, and severe allergic reactions like asthma.
LDL Cholesterol
This test is a risk marker for cardiovascular diseases. LDL is responsible for carrying cholesterol to cells. However, despite its good intentions, LDL is known as the “bad” cholesterol because, when levels are too high, it can cause the formation of plaque buildup in the arteries.
LDL Medium
Measures the amount of medium LDL particles in the blood. Elevated medium LDL levels are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
LDL Particle Number
Measures the number of LDL particles, which are the carriers of cholesterol. Too many LDL particles can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
LDL Pattern
Assesses the risk of cardiovascular disease based on cholesterol health, either Pattern A or Pattern B.
LDL Peak Size
Refers to the most common or average size of LDL particles in your blood. This is important because smaller LDL particles are more likely to contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
LDL Small
Small LDL particles in the blood are harmful, as elevated levels are linked to a higher risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
Lipoprotein (a)
About 50% of people who suffer heart attacks have a normal cholesterol level. Considering this, many cardiologists believe Lp(a) to be a major driver of cardiac events. This invaluable test is used by specialists but is not yet widely adopted in primary care. Lp(a) is a genetic marker that determines risk, particularly for those with symptoms or a family history of cardiovascular disease. Lipoproteins are made of lipids (fats) and proteins (energy) and are referred to as "sticky proteins."
Non-HDL Cholesterol
Measures cholesterol that is not HDL. This is a risk marker for dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Total Cholesterol
Total cholesterol numbers are part of a risk assessment for heart disease. Too much cholesterol in the blood can damage arteries and blood vessels and elevate the risk for stroke, heart attack, and heart disease. Cholesterol is a fatty substance produced by the liver to help with thousands of bodily functions, such as building cells, promoting hormone and brain function, and synthesizing vitamin D.
Triglycerides
The ratio of triglycerides to HDL measures risk for heart disease. Triglycerides are the most common type of fat in the body that stores excess energy from one's diet. An accumulation of triglycerides means there is too much fat in the blood and may indicate higher risk of a cardiac event.
High Blood Pressure
Hypertension can lead to coronary artery disease, where the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle become hardened and narrowed. This can cause chest pain (angina), a heart attack, or other serious conditions
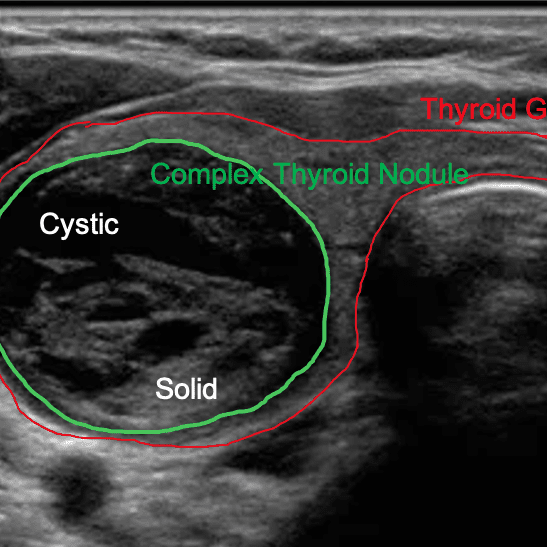
Your thyroid gland is like a thermostat that regulates your body's temperature. However, if produces too much or too little thyroid hormone, it can leads to various health issues.
Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TgAb)
This test checks for antibodies created against thyroglobulin, a protein produced and used by the thyroid gland to make T3 and T4 hormones, which control metabolism and tissue/cell growth. If present, it may indicate thyroid-related autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s.
Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPO)
This test checks for elevated antibodies created against thyroid peroxidase (TPO), an enzyme that helps produce hormones. Therefore, if antibodies are detected with this test, it can indicate thyroid-related autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s. Comparing this test with abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone may indicate Graves’ disease.
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
About 1 in 5 women and 1 in 10 men have hypothyroidism, and a TSH test can help reveal thyroid issues. Looking at abnormal TSH results alongside thyroid peroxidase (TPO) may be a sign of Graves’ disease. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and controls the release of thyroid hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
Thyroxine (T4) Free
This test is typically cross-referenced with TSH and T3 to gain insight into overall thyroid function. Thyroxine, or T4, is produced in the thyroid then released into the bloodstream where it travels to the liver and kidneys. It is converted into the hormone triiodothyronine (T3). The synergy of T4 and T3 is important for heart and digestive function, metabolism, brain development, bone health, and muscle control.
Triiodothyronine (T3) Free
T3 levels can reveal an overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism or Hashimoto’s) thyroid. T3 is the most powerful thyroid hormone in the body. It helps regulate body temperature, control heart rate, lower cholesterol, improve memory, promote regrowth after hair loss, soothe muscle aches, regulate bowel movements, and support fertility.
Iodine
Iodine levels give insight into thyroid health. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine to produce T4 and T3 hormones, to prevent goiters and help the body make protein and use oxygen. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Selenium
Selenium looks into the health of the liver, thyroid hormones, and kidneys. Selenium is a trace mineral found in soil that helps the body produce the antioxidant glutathione, which alleviates oxidative stress. It also stimulates thyroid hormones that aid in heart and digestive function, metabolism, brain and bone health, and muscle control. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Hypothyroidism
This is a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland failing to produce sufficient thyroid hormones, leading to a wide range of health issues including fatigue, weight gain, depression, cardiovascular problems, and impaired metabolic functions

Multi-cancer early detection (MCED) tests that can help screen for many of the deadliest cancers that don’t have recommended screening today.
Multi-Cancer Detection Test
Multi-cancer early detection test detects cancer signals across 50+ types of cancer as early as stage one. Test annually and stay vigilant for early warning signs. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), Free
Measuring one's PSA screens for tumors and/or monitors preexisting prostate cancer. On its own, it can not be used to diagnose cancer. Rather, this test and one's total PSA reveals the health of your prostate and acts as a signal if something is wrong.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) %, Free
This percentage helps determine the risk of prostate cancer and is often referred to if a doctor is deciding whether or not to conduct a biopsy. The percentage is calculated by dividing free PSA by total PSA and multiplying it by 100%.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), Total
Measuring one's PSA screens for tumors and/or monitors preexisting prostate cancer. On its own, it can not be used to diagnose cancer. Rather, this test and one's free PSA reveals the health of your prostate and acts as a signal if something is wrong.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that originates in the pigment-producing melanocytes, and it can cause severe health issues by rapidly spreading to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. With Forward, examine skin lesions and moles with the dermatoscope, design follow-up procedures, additional testing, or referrals to specialists if screening results are abnormal

Autoimmune disease is complicated. And on average, it takes 4.5 years to diagnose. We can identify and treat the condition behind your symptoms—usually within the first few visits.
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Pattern
The Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Pattern test analyzes the specific patterns of antibody staining on cells, providing detailed information that can aid in diagnosing and differentiating various autoimmune diseases. Different patterns, such as homogeneous, speckled, nucleolar, and centromere, are associated with specific autoimmune conditions, helping healthcare providers pinpoint the exact nature of the autoimmune response. This result is only processed if ANA screen is positive.
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Screen
The Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Screen is a blood test that detects the presence of antibodies that mistakenly target and attack the nucleus of the body's cells. A positive ANA test suggests an autoimmune response, but further tests are usually required to determine the specific condition and guide appropriate treatment.
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Titer
An ANA test assists in detecting autoimmune disorders. ANAs are autoantibodies produced by the immune system. While healthy antibodies protect the body from pathogens like viruses and bacteria, autoantibodies cause disease by mistakenly attacking healthy cells and tissues. This result is only processed if ANA screen is positive.
Rheumatoid Factor
Rheumatoid factors (RFs) are antibodies produced by the immune system. The presence of RFs can indicate autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid vasculitis, or Sjögren’s syndrome. Asymptomatic individuals with elevated RF levels may have pre-autoimmunity.
Celiac Disease (Comprehensive Panel)
Approximately 20% of people with celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, are asymptomatic. However, even without symptoms, untreated celiac disease may chip away at the immune system, which can lead to Type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, anemia, osteoporosis (due to issues with nutrient absorption), and skin conditions. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Celiac disease
This is an autoimmune condition triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When people with celiac disease eat gluten, their immune system reacts abnormally, damaging the lining of their small intestine.
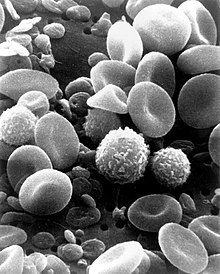
Immune regulation diseases occur when the immune system malfunctions, either by being overactive or underactive.
Basophils
Basophils account for only around 1% of white blood cells but play a role in allergy defense and stimulate antibodies against pathogens and parasitic organisms (such as ticks and worms) that cause injury or infection.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils are recruited to inflamed areas of the body to trap substances, kill infected cells, viruses, parasites, and bacteria, and help tame an allergic response. Testing can reveal issues in the digestive tract, specifically the esophagus, and includes both percentage and absolute levels.
Lyme Antibody
Lyme disease can go undetected (and therefore untreated) for years after initial infection. Testing for Lyme is incredibly important because it can eventually lead to brain and nerve damage. Lyme disease is the most common tick-borne illness in North America and is difficult to diagnose because its symptoms — more than 100 of them — can mimic other conditions like the flu, multiple sclerosis, lupus, and arthritis. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Lyme Antibody (IgG)
The Lyme IgM test is a blood test used to detect IgM antibodies in response to the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease. The presence of IgM antibodies indicates early-stage Lyme infection. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership. This result is only processed if Lyme Antibody is positive or equivocal.
Lyme Antibody (IgM)
The test is usually done with a Lyme IgG test for a more accurate diagnosis. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership. This result is only processed if Lyme Antibody is positive or equivocal.
Lymphocytes
Lymphocyte levels can reveal a number of conditions, including autoimmunity, bone marrow disorders, kidney disease, gastrointestinal disorders, and more. The role of lymphocytes in the body’s immune defense is so crucial that abnormal levels can weaken the body, leading to severe illness or impairing its ability to fight off infections. The test includes both percentage and absolute levels.
Monocytes
Like other white blood cells (WBCs), monocytes help the immune system destroy invaders and also facilitate healing and repair. Abnormal levels can indicate bacterial infections, virus or fungus, stress, chronic infections, or autoimmune disorders. The test includes both percentage and absolute levels.
Neutrophils
Testing the quantity of neutrophils helps detect damage caused by inflammatory disorders (such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout), infections (both acute and chronic), certain cancers (such as myelocytic leukemia), and physical stressors (including eclampsia in pregnant women, injury, and burns). Neutrophils are key patrols and first responders in the immune system, attacking antigens they encounter. The test includes both percentage and absolute levels.
White Blood Cell Count
A healthy WBC baseline over time correlates with the body's ability to fight off diseases and other hazards. Prolonged abnormalities can negatively affect biological age by impairing healing and increasing the risk of illness.
High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
hs-CRP is revelatory in one's overall health as it relates to the risk of inflammation-related diseases. Chronic inflammation is linked to every major disease: heart disease (even before symptoms occur), type 2 diabetes, cancer, high blood pressure, Alzheimer’s, depression, all autoimmune diseases, and severe allergic reactions like asthma.
Psoriasis
This is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes skin cells to grow too quickly. This rapid growth leads to a buildup of thick, scaly patches on the skin's surface. These patches can be itchy, painful, and sometimes even embarrassing.

Biomarker analysis, and other data to create customized health plans tailored to individual women's needs and risk factors. This can help identify and address potential health concerns early on.
Anti-Mullerian Hormone
AMH is a key fertility marker that assesses ovarian reserve (egg count) at the time of the test. This test sheds light on the body’s potential to produce eggs for fertilization, particularly if one is nearing menopause or experiencing a hormonal condition such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or primary ovarian insufficiency (POI).
Pregnancy (hCG)
A positive beta human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level is used for early detection of pregnancy. Pregnancy tests detect the hCG hormone in both blood and urine. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Sex Hormone Binding Globulin
When SHBG levels change, it can impact the amount of available hormones in the body, either too much or too little. This can affect the menstrual cycle as well as fertility. SHBG patrols the amount of sex hormones the body tissues can use.
Testosterone, Free (female)
This helps evaluate functions associated with testosterone levels, such as fertility, sexual function, muscle mass, energy, mood, insulin resistance/sensitivity, and pituitary function. It can also detect prediabetes, PCOS, or menopause. Function tests both "free" and “total” testosterone in the blood.
Testosterone, Total
In all adults, healthy levels of testosterone are important for general health, body composition, sexual function, and reduced risk of disease. Function tests both "free" and “total” testosterone in the blood.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) (female)
FSH evaluates ovarian health and pituitary function, and can help determine a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), perimenopause, or menopause. As a type of protein hormone, FSH is responsible for stimulating the ovarian follicles that produce and release eggs during ovulation. If one is on hormonal birth control, this test will not be run.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) (female)
LH levels give insight into sexual development and fertility. LH releases estrogen during the menstrual cycle, which triggers the release of an egg from the ovary**, otherwise known as ovulation.** It can also help determine states of perimenopause and menopause. If one is on hormonal birth control, this test will not be run.
Prolactin (female)
Prolactin levels can guide the diagnosis of irregular or absent menstrual periods, infertility, menopausal symptoms, osteoporosis, liver or kidney disease, hypothyroidism, and/or estrogen and testosterone deficiency, in addition to unwanted lactation. It is also used to screen for pituitary tumors. Prolactin is a peptide hormone produced by the pituitary gland and stimulates breast development and milk production in pregnant women.
Estradiol (E2) (female)
For biological females, testing the hormone estradiol (one type of estrogen) is key in detecting menopause, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), androgen- or estrogen-producing tumors, uterine and breast cancer, and mitigating the risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease. If one is on hormonal birth control, this test will not be run.
DHEA-Sulfate (female)
DHEA Sulfate, the most abundant hormone in the human body, is associated with longevity, positive reproductive outcomes, and immune system regulation. This test can gauge reproductive function and the health of your adrenal gland.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a common condition that affects millions of women worldwide. While the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Treatment for PCOS can vary depending on the individual's symptoms.

Biomarker analysis, and other data to create customized health plans tailored to individual men's needs and risk factors. This can help identify and address potential health concerns early on.
Testosterone, Total
In all adults, healthy levels of testosterone are important for general health, body composition, sexual function, and reduced risk of disease. Function tests both "free" and “total” testosterone in your blood. One will naturally have a higher level of "total" than "free.”
DHEA-Sulfate (male)
DHEA-S can gauge the health of the reproductive system and adrenal glands. It is one of three adrenal androgens: steroid hormones that control the development and maintenance of masculine characteristics.
Estradiol (E2) (male)
For biological males, testing the hormone estradiol (one type of estrogen) is key in understanding testosterone levels and sexual function. Estradiol is essential in sexual development and managing the reproductive system.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) (male)
FSH levels share insight into one's fertility, along with testicle and pituitary health. Strong levels are necessary for healthy male hormonal function, and are partially responsible for sperm production and sexual development.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
LH helps the testicles make testosterone, which is important for producing sperm and many other male functions. LH levels gives insight into one's sexual development and fertility.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), Free
Measuring one's PSA screens for tumors and/or monitors preexisting prostate cancer. On its own, it can not be used to diagnose cancer. Rather, this test and one's total PSA reveals the health of your prostate and acts as a signal if something is wrong.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) %, Free
This percentage helps determine the risk of prostate cancer and is often referred to if a doctor is deciding whether or not to conduct a biopsy. The percentage is calculated by dividing free PSA by total PSA and multiplying it by 100%.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), Total
Measuring one's PSA screens for tumors and/or monitors preexisting prostate cancer. On its own, it can not be used to diagnose cancer. Rather, this test and one's free PSA reveals the health of your prostate and acts as a signal if something is wrong.
Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG)
DHEA Sulfate, the most abundant hormone in the human body, is associated with longevity, positive reproductive outcomes, and immune system regulation. This test can gauge reproductive function and the health of your adrenal gland.
Prolactin (male)
Prolactin levels can guide diagnosis of low libido or erectile dysfunction, or screen for pituitary tumor. Prolactin is a peptide hormone produced by the pituitary gland.
Testosterone, Free (male)
This helps evaluate functions associated with testosterone levels, such as fertility, sexual function, muscle mass, energy, mood, insulin resistance/sensitivity, and pituitary function. It can also screen for prediabetes. Function tests both "free" and “total” testosterone in the blood.
Erectile dysfunction (ED)
ED is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection that is firm enough for sexual intercourse. It is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide.

Metabolic deseases are disorders that affect how the body processes food and turns it into energy. These diseases can disrupt the body's metabolism, leading to a variety of health problems.
Insulin
Insulin levels can uncover reasons behind abnormal blood sugar, insulin resistance, and more. It can also reveal hidden blood sugar issues even years before they escalate to something like diabetes. Establishing one's insulin baseline can be incredibly insightful to how one's lifestyle affects health.
Leptin
Leptin tells the brain when to stop eating. It is a hormone created by fat cells that regulates energy expenditure, and this test is an important diagnostic tool for leptin deficiency, which causes obesity and chronic inflammation. High levels are often associated with vascular risk factors, including insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension.
Uric Acid
Uric acid in the blood screens for metabolic disorders, like gout, anemia, and immunodeficiencies. This often overlooked test has renewed attention after recent studies show elevated levels can increase the risk of death from cardiovascular issues by 39% and stroke by 35%.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
HbA1c is the average amount of glucose attached to blood cells over the last 90 days. It diagnoses, monitors, and screens for prediabetes and diabetes. This test is a revelatory look into one's health, specifically the body’s ability to control blood sugar. Unhealthy levels are triggered by inflammation, vitamin deficiencies, kidney damage, thyroid disorders, and more. One's diet and habits can have a substantial impact on this test.
Glucose
Too much glucose (hyperglycemia) is a major driver of many diseases and illnesses, including cancer, diabetes, high blood pressure, heart attacks, kidney disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Glucose is a type of sugar (from food) that the body uses for energy. When glucose is not absorbed and used, it can form glycogen and be stored as fat in the liver. Over time, this can lead to a decline in overall health.
Adiponectin
Adiponectin abnormalities are an indicator of metabolic disorders, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Adiponectin is a growth hormone, like prolactin and insulin, that influences body weight and metabolism by combating inflammation, regulating glucose, metabolizing lipids, and controlling insulin response. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Obesity
This is a chronic condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation. It is a complex disease with multiple contributing factors, including genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors.

While aging is a natural biological process, chronic stress can significantly accelerate it, leading to premature aging and a higher risk of age-related diseases.
Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1)
IGF-1 is known as the "growth hormone" because it stimulates growth in cells throughout the body. This leads to growth and development (from the womb and through adolescence), strengthening of tissues (e.g. improving bone density, building muscle), and healing (e.g. skin, bones, gut lining), depending on what the body needs. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the $499 membership.
Biological Age
Biological age reflects how one's body is aging at the cellular and molecular levels, which can determine the risk of age-related conditions like cardiovascular diseases and cognitive decline. Unlike calendar age (number of years lived), biological age is reversible and something one can optimize. It calculates mortality risk and phenotypic age based on various lab test results. While biological age on its own might seem like a vanity metric, when combined with 100+ lab tests, it offers a comprehensive benchmark for tracking and enhancing health and longevity.
Cortisol
Cortisol, for one, is often referred to as “the stress hormone.” However, it goes beyond stress to help the body with numerous functions. Testing can detect imbalances in adrenal function.
DHEA-Sulfate (female)
DHEA Sulfate, the most abundant hormone in the human body, is associated with longevity, positive reproductive outcomes, and immune system regulation. This test can gauge reproductive function and the health of your adrenal gland.
Cortisol deficiency
This is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol, a hormone that helps the body regulate stress, blood sugar, and blood pressure. It can also affect the production of aldosterone, a hormone that regulates blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
Nutrients are essential substances found in food that the body needs to grow, repair tissues, and function properly. They provide energy, build and maintain cells, and support various bodily functions.
Arachidonic Acid/EPA Ratio
This ratio helps assess inflammation and the management of heart disease and other chronic/inflammatory processes.
Calcium
Calcium levels help understand symptoms related to the kidneys, bones, thyroid, parathyroid, or nerves. Calcium is a mineral the body uses to build and maintain strong bones, teeth, muscle control, and blood circulation.
Copper
Healthy copper levels are important because copper is a vital mineral that helps the body metabolize iron and make and regenerate melanin, bones, and connective tissues, among other essential processes. However, untreated copper toxicity can become hazardous to the heart, kidneys, liver, and brain. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Ferritin
Ferritin levels can help diagnose iron deficiency, liver disease, inflammation, or insulin resistance. Ferritin is a protein that stores iron in cells and then releases the iron when the body makes more red blood cells.
Homocysteine
A homocysteine test checks the body’s vitamin B levels and methylation function, a key biochemical process essential for almost all of the body’s systems. Abnormal homocysteine can build up and increase the risk of blood clots, dementia, osteoporosis, heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. Homocysteine is an amino acid that helps organs grow and regenerate.
Iodine
Iodine levels give insight into thyroid health. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine to produce T4 and T3 hormones, to prevent goiters and help the body make protein and use oxygen. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the $499 membership.
Iron
Healthy iron levels create vitality throughout the entire body. Iron helps various vital functions, like providing energy and focus, building a strong gastrointestinal tract and immune system, and regulating body temperature. Iron deficiency can lead to numerous biological problems, including anemia.
Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
TIBC assesses the body’s ability to transport iron in the blood, and can diagnose and/or monitor iron-deficiency or iron overload. Lower than normal levels of TIBC could indicate too much iron and a variety of conditions, including anemias, inflammation, or liver disease.
Iron % Saturation
The Iron % Saturation test measures the percentage of transferrin, a protein that transports iron in the blood, that is saturated with iron. This test is crucial for assessing iron status in the body and can help diagnose conditions such as iron deficiency anemia or iron overload disorders like hemochromatosis.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral imperative for cells to make energy, for chemical pumps to work and stabilize membranes, and to help muscles relax. Low magnesium can impact calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and/or parathyroid hormone. This test helps evaluate absorption and helps determine whether or not there’s a problem with kidney function or the gastrointestinal tract.
Methylmalonic Acid (MMA)
MMA measures vitamin B12 and can detect a deficiency even when mild or just beginning. MMA is a key component for metabolism and energy, and because blood and/or urine levels of MMA rise when B12 levels drop, it is a more sensitive biomarker than testing just B12 levels.
Omega-3: EPA+DPA+DHA
Measures the amount of DHA, DPA, and EPA, omega-3 essentials for brain function and development. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits.
Omega-3: EPA+DPA+DHA
Measures the amount of DHA, DPA, and EPA, omega-3 essentials for brain function and development. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits.
Omega-6: Arachidonic Acid
Measures this pro-inflammatory omega-6 fatty acid, which can increase the risk of inflammatory diseases and mood disorders if chronically elevated. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits.
Omega-6: Linoleic Acid
Linoleic acid is a key omega-6 fatty acid essential for cell membrane structure and function and is a precursor to arachidonic acid, which plays a significant role in the body's inflammatory processes. Elevated levels of linoleic acid can indicate excessive dietary intake, which may contribute to chronic inflammation and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits.
Omega-6 / Omega-3 Ratio
While omega-6 is typically higher than omega-3, ensuring that this ratio remains low is important. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits.
Omega-6 Total
Imbalanced omega-3 and omega-6 levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, age-related macular degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and more. Omegas are essential fatty acids (EFAs), which are the building blocks for every cell in the body. Well-balanced omegas can contribute to optimal brain performance, mental health, nerve function, a healthy heart, circulation, immune system, gastrointestinal tract, skin, hair, and nails. To ensure timely results, this test may be completed during Mid-Year visits.
Selenium
Selenium looks into the health of the liver, thyroid hormones, and kidneys. Selenium is a trace mineral found in soil that helps the body produce the antioxidant glutathione, which alleviates oxidative stress. It also stimulates thyroid hormones that aid in heart and digestive function, metabolism, brain and bone health, and muscle control. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the $499 membership.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency is widely underdiagnosed and undertreated. Over time, low levels can lead to hypothyroidism, osteoporosis, cancer, heart disease, fatigue, depression, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), gut issues, and fibromyalgia. The role of vitamin D is vast and benefits the immune system, thyroid, bones and teeth, muscles, and brain.
Zinc
Zinc is mostly known for its immune support, but it's actually a powerful mineral across all systems of the body: from strengthening bones and muscles, preventing blood clotting and metal accumulation, promoting proper insulin and thyroid function, and so much more. If deficient, it can impact mood, sexual function, and immunity.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is linked to osteoporosis, increased risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, and potential immune system irregularities

We analyze urine sediments to identify potential abnormalities, assess kidney function, and mitigate associated risks, thereby contributing to a healthier and longer lifespan.
Albumin - Urine (Microalbumin)
Albumin is a foundational protein found in the blood. In early kidney damage—most commonly from hypertension or type 2 diabetes—smaller fragments of albumin called microalbumin appear in the urine.
Appearance
Checks the clarity of urine from clear to turbid.
Bacteria
Healthy urine is sterile, so when bacteria is present, it's a sign of infection.
Bilirubin
Look into the general health of the liver. When healthy, the liver makes bile, which contains bilirubin. This bile helps digest food, and a thriving liver gets rid of excess bilirubin, but when the liver isn't working properly, bilirubin builds up.
Clarity
The clarity of urine, from clear to turbid, explores the health of one's kidneys and urinary tract.
Color
An unusual urine color can be a sign of disease, such as a kidney disorder or urinary tract infection (UTI). The scale from light to dark gives a picture of how much water is being flushed through a system.
Glucose-Urine
If one is healthy, glucose levels in the urine are generally too low to be detected. Glucose in the urine, or glucosuria, is a symptom of both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes (when one's blood sugars are high), pregnancy, or liver abnormalities or hormonal disorders.
Hyaline Casts
It's ok if hyaline casts show up in urine. However, large amounts of them may indicate kidney damage due to decreased blood flow to the kidneys.
Ketones
Ketone testing can help diagnose ketoacidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a complication of diabetes, or issues unrelated to diabetes like gastrointestinal diseases (IBS, colitis, Crohn’s, celiac, GERD). Ketones are produced in the liver as part of a body’s metabolism process. If one is low on glucose, the body burns fat for energy instead and produces ketones, which show up in urine. This is the process behind ketogenic (keto) diets.
Leukocytes
Leukocytes are white blood cells (WBCs), which are vital to health! However, if they're detected in urine, it may be a sign of inflammation in the urinary tract or kidneys.
Nitrite
Increased nitrites in urine can indicate an infection in the urinary tract, anywhere from the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Healthy urine has chemicals called nitrates. When bacteria enter the urinary tract, nitrates can transform into nitrites.
Occult Blood
This test detects blood in urine, which could potentially indicate a urinary tract infection (UTI), enlarged prostate, kidney damage (from injury), kidney disease, or other kidney or bladder-related conditions.
pH
The goal of testing pH is to identify whether or not one has an acid-base imbalance, to determine how severe the imbalance is, and to help diagnose underlying diseases or conditions (such as diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening complication of diabetes). Testing also helps monitor critical illnesses that affect acid-base balance, such as chronic lung disease and kidney disease.
Protein
The goal of this test is to evaluate kidney function. Normally, protein stays in the blood and doesn't pass into urine. The kidneys prevent this from happening. If proteinuria (protein in urine) is detected, the kidneys aren't functioning properly.
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and return carbon dioxide for exhalation. This test helps detect conditions such as anemia, dehydration, and polycythemia. Abnormal RBC levels can indicate various health issues, including nutritional deficiencies, bone marrow disorders, and chronic illnesses.
Specific Gravity
Specific Gravity is the concentration of the urine, which is a quick way to tell if the kidneys are trying to compensate for an abnormality. This test helps convey overall kidney health and can screen for renal tubular necrosis, diabetes insipidus, kidney failure, low levels of sodium in the blood, or a severe kidney infection.
Squamous Epithelial Cells
It's normal to have a small amount of epithelial cells in urine. A large amount, however, may indicate an infection, kidney disease, or another serious medical condition.
White Blood Cell (WBC)
White blood cells play a vital role in defending the body against infections, inflammation, and diseases. This test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as infections, leukemias, autoimmune disorders, and bone marrow disorders. Abnormal WBC counts can indicate an active infection, an immune response, or an underlying medical condition.
Yeast
The presence of yeast in urine suggests a potential fungal infection, commonly due to Candida species, and may indicate a urinary tract infection (UTI) or a vaginal yeast infection.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
This is a progressive condition that damages the kidneys over time, leading to decreased kidney function. This damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including: Diabetes, High blood pressure, Glomerulonephritis, Polycystic kidney disease.

Food and environmental allergies can cause digestive, respiratory, skin, and fatigue-related issues. Testing for sensitivities and allergens helps identify triggers, guiding dietary and environmental adjustments to reduce symptoms and improve health.
Food Allergy Profile (IgE)
The IgE allergy test looks at whether you are susceptible to the classic food allergies: peanuts, tree nuts, dairy, eggs, gluten, soy, fish, and shellfish. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the $499 membership.
Indoor & Outdoor Allergy Profile (IgE)
Tests susceptibility to allergens commonly found in mold, dander, mouse dust, insects and venom, storage mites, and select grasses, trees, and weeds based on one's region. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the $499 membership.
Allergic rhinitis (hay fever)
A condition that causes inflammation of the nasal passages and sinuses, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and congestion.

The liver, as a sophisticated metabolic hub, is instrumental in maintaining optimal health. Its intricate functions, including detoxification, nutrient processing, and protein synthesis, are vital for longevity.
Alanine Transaminase (ALT)
ALT is an enzyme that checks on liver health. If one's liver cells are damaged due to excess alcohol, drugs, disease, or injury, ALT will appear in the bloodstream and, therefore, in a blood test.
Albumin
Abnormal albumin can indicate malnutrition, liver or kidney disease, or a digestive inflammatory condition (Crohn’s or Celiac) resulting in malabsorption. Albumin is a protein made by the liver that helps fluid remain in the bloodstream rather than leaking into other tissues. It also helps hormones, vitamins, and enzymes transfer throughout the body to their final destinations.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
This percentage helps determine the risk of prostate cancer and is often referred to if a doctor is deciding whether or not to conduct a biopsy. The percentage is calculated by dividing free PSA by total PSA and multiplying it by 100%.
Aspartate Transaminase (AST)
AST is an enzyme mostly found in the liver and helps metabolize amino acids. Testing for AST in the blood can help detect liver damage from injury or a number of diseases and conditions, like hepatitis, cirrhosis, mononucleosis, or other liver diseases, heart problems, or pancreatitis.
Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
Monitor liver health with GGT. This test helps detect liver disease, identify bile duct blockages, and check for conditions related to alcohol and toxins. The GGT biomarker is a reliable detector (but not a diagnostic test) for toxin exposure or fatty liver from alcohol, even when other liver tests are normal.
Total Bilirubin
In tandem with a full liver panel, this test can help determine the cause of jaundice and/or help diagnose conditions such as liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or blockage of the bile ducts. The liver makes bile to help digest food, and bile contains bilirubin. A healthy liver can get rid of bilirubin, but when the liver isn't working properly, it cannot break down bilirubin and dispose of it.
Total Protein
Protein levels explore the health of the kidneys, liver, and absorption processes. The human body is made up of thousands of proteins, all of which have various roles in making and maintaining every cell in the body, including enzymes and hormones. Proteins also fuel those cells and the immune system with energy.
Globulin
Globulin is a protein essential for liver function, blood clotting, and immune system operations. Abnormal globulin levels can indicate various conditions, such as liver disease, autoimmune disorders, or chronic infections.
Cirrhosis
This is a chronic liver disease caused by ongoing damage to the liver. As the liver damage progresses, scar tissue forms and replaces healthy liver tissue. This scarring can interfere with the liver's ability to function properly, leading to a variety of health problems.
While there is no cure for cirrhosis, targeted therapies can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.

The kidneys, as sophisticated filtration units, are indispensable for maintaining optimal health. Their intricate functions, including waste removal, fluid balance, and hormone production, are vital for longevity.
Albumin (Microalbumin) - Urine
Keep an eye on kidney health with microalbumin. This test checks for small fragments of albumin in one's urine, which may be an early indication of kidney damage due to hypertension or type 2 diabetes. Microalbumin will show issues even before the normal kidney tests (creatinine and BUN) are elevated.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Urea nitrogen is a waste product that the kidneys flush out, but the presence or buildup of urea nitrogen waste in the blood means the kidneys aren't regulating waste properly. Compared to one's creatinine levels, this test can screen for kidney disease.
BUN / Creatinine Ratio
This ratio helps evaluate kidney function and can indicate conditions such as dehydration, kidney disease, or issues affecting kidney perfusion. A high ratio may suggest dehydration or upper gastrointestinal bleeding, while a low ratio can point to acute tubular necrosis or liver disease. This result is only calculated if BUN is out of range.
Calcium
Calcium levels help understand symptoms related to the kidneys, bones, thyroid, parathyroid, or nerves.
Chloride
Chloride is a mineral in the body that creates channels in cell membranes to carry out vital tasks. This test can help detect dehydration, kidney disease, liver disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, or other disorders.
Sodium
A sodium test looks at electrolytes and pH. When sodium levels are abnormal, it can signal issues with the brain, lungs, liver, heart, kidneys, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
Creatinine
Creatinine levels vary from person to person, but abnormalities typically signal kidney disease or damage. One's creatinine levels are directly related to lifestyle, diet, medication, and how those can impact the kidneys’ ability to function. Creatinine (not to be confused with creatine) is a chemical compound left over from everyday wear and tear of the muscles.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR)
eGFR is a kidney biomarker, and this test is used to help diagnose kidney disease at an early stage when it is most treatable. It can also track those with pre-existing kidney-related conditions.
Potassium
Potassium is an electrolyte that aids in muscle contraction, digestion, messaging from the brain to the body, and regulating fluids and blood pressure. Potassium levels can help detect kidney, liver, heart, and blood disorders.
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can damage the blood vessels throughout the body, including the kidneys. Over time, this damage can lead to inflammation and scarring of the kidneys, which can reduce their ability to filter waste products from the blood.

The pancreas, as a metabolic regulator, is instrumental in maintaining optimal health. Its convoluted functions, including insulin production and digestive enzyme secretion, are vital for glucose homeostasis and nutrient absorption.
Amylase
Amylase checks in on the pancreas, and irregular levels can detect salivary disease, celiac disease, IBD, and the growth of a tumor in an amylase-producing tissue. Amylase is an enzyme produced in the salivary glands and pancreas. It’s a digestive protein that breaks down carbohydrates and starches into simple sugars, giving the body energy.
Lipase
A lipase test is able to show swelling or inflammation in the pancreas, a condition known as pancreatitis. It can also reveal other health conditions such as kidney disease, pancreatic cancer, and problems with the gallbladder or esophagus. Lipase is an enzyme produced by the pancreas that helps the body digest fats.
Pancreatitis
This is a condition in which the pancreas becomes inflamed. The pancreas is an organ located behind the stomach that producesdigestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin. When the pancreas becomes inflamed, these enzymes can leak into the surrounding tissues, causing pain and damage.
Heavy metal pollution, as a insidious environmental toxin, can wreak havoc on the body's delicate systems. Its insidious effects, including oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and organ damage, can compromise overall health and longevity.
Mercury
Mercury is a neurotoxin that can result in kidney damage, brain damage, and fertility issues. It is found everywhere: fish, coal, plastics, pesticides, mercury amalgam dental fillings, and more. In 2022, the US government reaffirmed regulations to curtail mercury pollution from power plants. Testing mercury levels over time and establishing a baseline provides an understanding of why and how one may be exposed to mercury.
Aluminum
The form of aluminum that causes harm is present in many everyday household and personal care products. An aluminum test detects whether or not there has been an overexposure to aluminum. Too much impairs iron absorption and can lead to faulty hematopoiesis--the process through which the body makes red blood cells. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Arsenic
Arsenic is a neurotoxin that can lead to hypertension, infertility, neurological disorders, and peripheral neuropathy (pain in the hands and feet). Arsenic comes in two forms: organic and inorganic, used in manufacturing and mining. Arsenic can be found in seafood, wine, groundwater, and more. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the $499 membership.
Lead
Lead is a common element all around us and is naturally absorbed, but it can be dangerous if exposed to hazardous sources. Untreated toxicity can lead to fertility complications, kidney failure, convulsions, cardiovascular issues, hormonal disruption, gastrointestinal issues, and neurological changes.
Reproductive problems
The effects of heavy metal pollution on reproduction can vary depending on the type of metal, the level of exposure, and the individual's susceptibility. They could be associated to reduced sperm count and motility, or couple's infertility.
Blood, as the vital fluid circulating throughout the body, plays a multifaceted role in maintaining optimal health, including oxygen and nutrient delivery, waste removal, immune defense, and hormonal regulation.
ABO Group and Rhesus (Rh) Factor
Know your blood type! This information is important not only in case of an emergency where one might need a blood transfusion but also if you want to donate blood to help others. Blood type is also a predictor for some conditions that occur during pregnancy and/or if one is susceptible to blood clotting or kidney stones.
Hematocrit
As part of the complete blood count, an HCT test measures the percentage of red blood cells in the blood. This test helps screen for, diagnose, and monitor conditions that affect the blood or bone marrow.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin reflects the number of red blood cells active in the blood. Low levels may uncover anemia, vitamin deficiencies, loss of blood (both internal and external), and chronic diseases. The test can also help detect diseases affecting the lungs, liver, kidneys, or cardiovascular system, significant long-term infection, cognitive impairment, and certain types of cancer, and diagnose chronic blood disorders.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
MCHC measures the amount of hemoglobin per unit volume. So, this test assesses the hemoglobin content within the volume of the cell, which can uncover iron-deficiency anemia, hypothyroidism, spherocytosis, or RBC agglutination.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)
MCH is usually done as part of the complete blood count and can help detect various types of anemia (deficiency in iron, B12, or folate), blood loss, cancer, kidney or liver disease, or autoimmunity. MCH measures the average amount of hemoglobin in the red blood cells.
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
MCV's insight into the blood is a unique indicator of overall health. If MCV is either high or low overtime (most likely indicating a chronic vitamin deficiency or blood condition), it can degrade the body's general wellness and thus one's phenotypic age. MCV measures average size of red blood cells: whether they are too big, too small, or just right.
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) measures the mass of platelets, which is important in determining the cause of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count) or thrombocytosis (a high platelet count). So, why does MPV matter? When platelets are healthy, there is a dynamic relationship between their size and count.
Platelet Count
Abnormal platelet count is a risk marker for heart attack, stroke, and other heart diseases, but this test can also help diagnose autoimmune disease, bone marrow damage (which can be caused by certain cancers, such as leukemia and/or cancer treatments), spleen disorder, and parasites. Platelets, which are made in the bone marrow, are small, colorless blood cells that form clots with the goal of stopping or preventing bleeding.
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count
RBC count can reveal various anemias, vitamin deficiencies, colon, bladder, or kidney issues, chronic diseases that cause bone marrow suppression, autoimmune disorders, blood disorders, polycythemia vera, congenital heart disease, and more.
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
RDW is the size and volume of the red blood cells. RDW and MCV explore one's overall health, and together, they can detect liver disease and various types of vitamin-deficiency anemias even before symptoms occur. When either or both are abnormal over time, it can lead to a higher risk of disease and increase one's phenotypic age.
Sickle cell disease
This is a genetic disorder that causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped. In people with sickle cell disease, the hemoglobin in red blood cells is abnormal, which causes the cells to become rigid and sticky. These misshapen cells can block blood flow to parts of the body, leading to pain, anemia, and other complications.

Electrolytes, as the vital currency of cellular function, are involved in fluid balance, nerve impulse transmission, and muscle contraction; essential for longevity.
Calcium
Calcium levels help understand symptoms related to the kidneys, bones, thyroid, parathyroid, or nerves.
Chloride
A chloride test is useful in diagnosing the underlying causes of abnormal fluid levels or pH balances, such as dehydration, kidney disease, liver disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, or other disorders. Chloride is a major mineral in the body that manufactures channels in cell membranes, which carry out different vital tasks.
Magnesium, RBC
Magnesium is a mineral imperative for cells to make energy, for chemical pumps to work and stabilize membranes, to help muscles relax, and so much more.
Potassium
Potassium levels can detect kidney disease, liver disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, or other disorders. As an electrolyte, potassium helps muscles contract, aids digestion, allows nerves to transport messages from the brain to the body, and balances fluids and regulates blood pressure.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (bicarbonate) levels monitor pH and/or electrolyte balance. When irregular, it can be a sign of dehydration, kidney disease, liver disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, or other disorders. Bicarbonate is an alkali of the electrolyte family. As an alkali, it plays a role in balancing the acid-base in pH balance.
Sodium
A sodium test looks at electrolytes and pH. When sodium levels are abnormal, it can signal issues with the brain, lungs, liver, heart, kidneys, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
Hyponatremia
This is a condition characterized by low blood sodium levels. Sodium is a mineral that is essential for many bodily functions, including regulating fluid balance, nerve impulses, and muscle contractions.
When the body has too much water relative to sodium, the blood sodium levels can become diluted, leading to hyponatremia. This can occur in a variety of situations, including: kidney problems, hormone imbalances and more.

Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype, is a genetic blueprint for lipid metabolism, plays a significant role in cardiovascular health. Its variants influence cholesterol levels and risk for Alzheimer's disease
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) Genotype
ApoE is a predictive genetic biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease, currently one of the leading causes of death in the United States. The result of this test illuminates personal risk, even decades before the onset of the disease. Holding this wisdom, along with the health of a brain's support systems (many of which are part of your Function biomarkers), can potentially help avert onset completely. *This add-on test is available for an additional cost and is not included in the basic membership.
Alzheimer's disease
This is is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss, confusion, and other cognitive problems. It is the most common form of dementia, a condition that affects memory, thinking, and behavior.

Biological age, analogous to a personalized health score, reflects the body's overall state and its resilience to aging-related challenges. It is a more accurate indicator of health than chronological age.
Biological Age
Biological age reflects how the body is aging at the cellular and molecular levels, which can determine the risk of age-related conditions like cardiovascular diseases and cognitive decline. Unlike calendar age (number of years lived), biological age is reversible and something one can optimize. It calculates mortality risk and phenotypic age based on various lab test results. While biological age on its own might seem like a vanity metric, when combined with 100+ lab tests, it offers a comprehensive benchmark for tracking and enhancing health and longevity.
Sarcopenia
This is a progressive condition characterized by the loss of muscle mass and strength. It is a natural part of aging, but it can also be accelerated by other factors such as inactivity, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions.

1
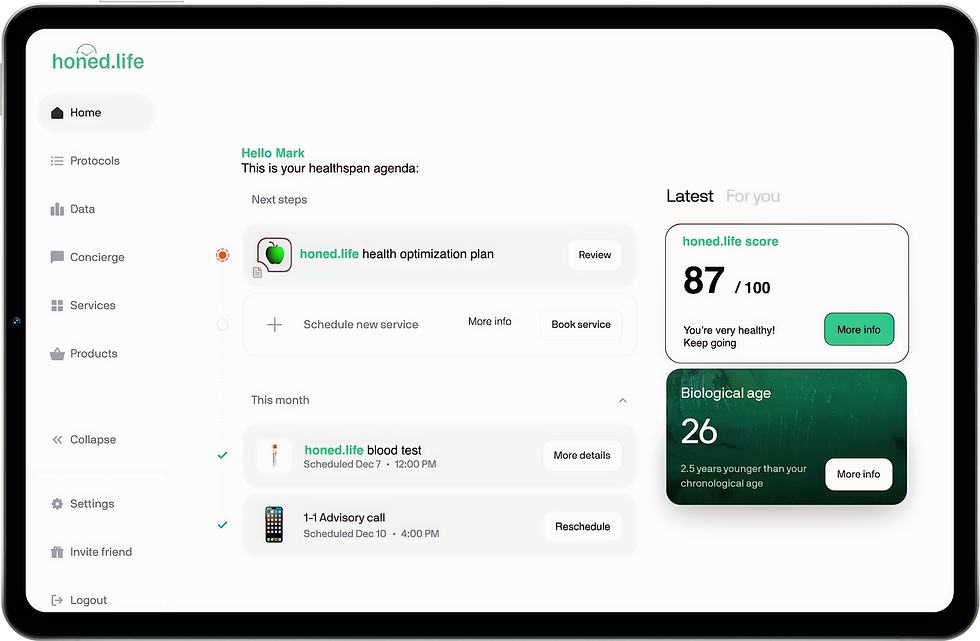
dashboard
Our virtual longevity clinic's client dashboard is fully intuitive, offering seamless navigation and effortless access to health insights, appointments, services, and personalized longevity plans.
INTUITIVE DASHBOARD
2
biomarkers range
Our app user experience ensures effortless access to biomarker ranges, providing clear, immediate navigation for quick insights and personalized health tracking.
EASY ACCESS TO PERSONAL BIOMARKERS

3
data scores
Our app offers seamless access to organ, wellness, and disease risk scores, delivering a clear and user-friendly experience for instant insights and proactive health management.
50+ ORGANS HEALTH SCORES
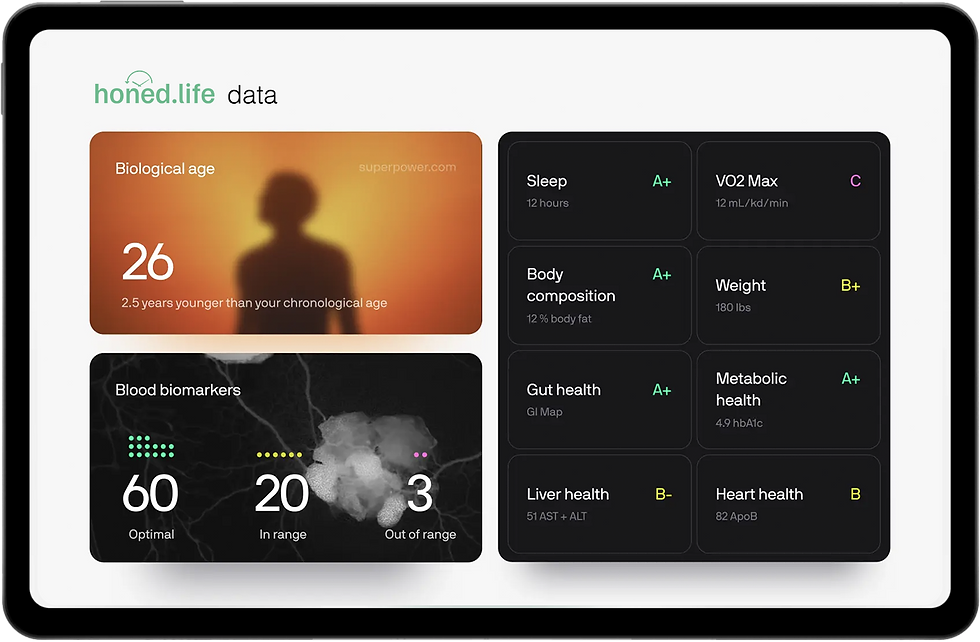
4
health data
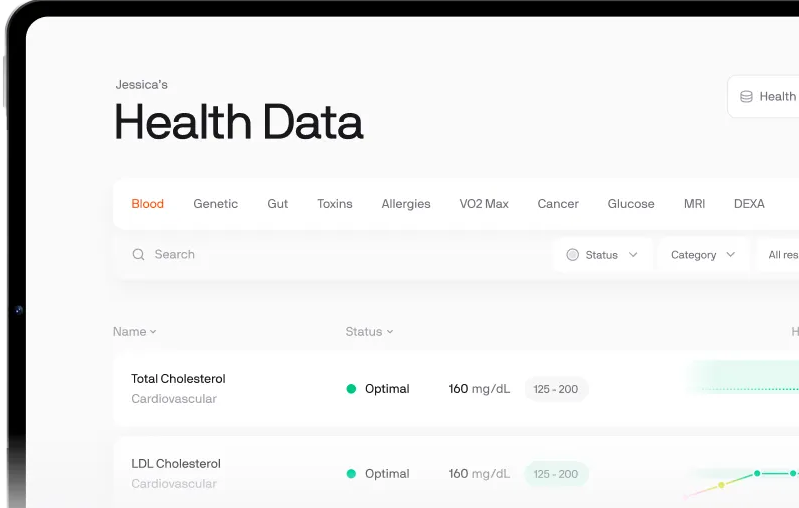
Our app ensures seamless access to 100+ test results, providing a clear and user-friendly experience for immediate insights and personalized health monitoring.
100+ HEALTH TESTS DATA
5
clinicians access
Our app enables seamless access to specialized clinicians in longevity science and all medical specialties, ensuring a smooth and efficient experience for expert guidance and personalized care.
OUR CLINICIANS AT YOUR FINGER TIPS

6
services access
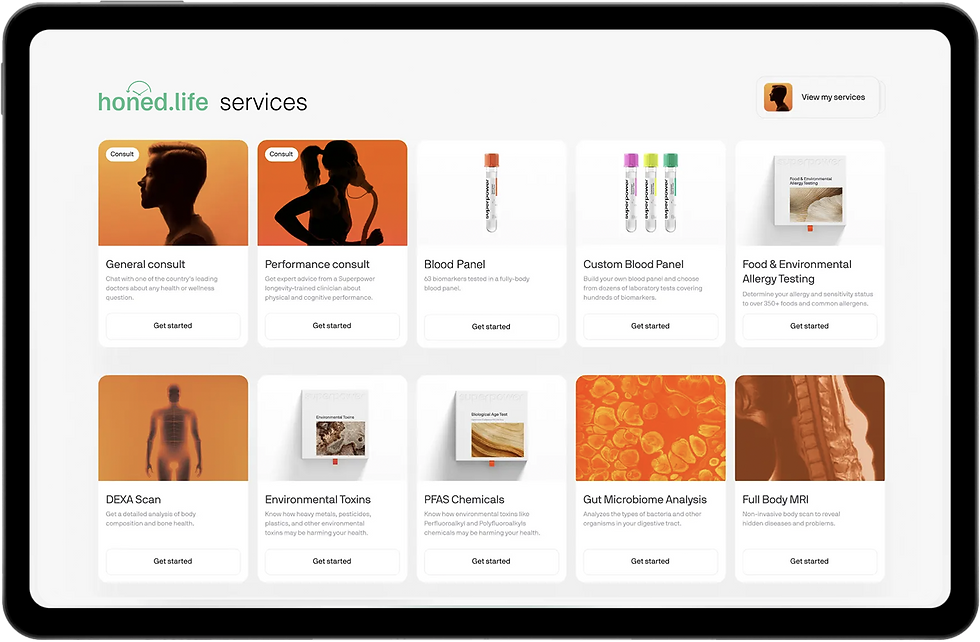
Our app ensures fast access to services, including MRI imaging, tests, proactive diagnostics, scheduling, and our marketplace, providing a smooth and efficient experience for comprehensive health management.
YOU ARE IN CONTROL WITH HONED LIFE SERVICES

1
Gene Therapy
2 ONGOING RESEARCH PROJECTS
Senolytics: These are compounds that selectively eliminate senescent cells, which contribute to aging and age-related diseases. By removing these dysfunctional cells, honed.life researchers hope to improve tissue health, prevent chronic conditions, and extend lifespan.

2
Oncology
4 ONGOING RESEARCH PROJECTS
Immunotherapy: This approach harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer cells. By enhancing immune function or engineering immune cells to target cancer, honed.life researchers aim to develop more effective and less toxic cancer treatments.

3
Drug Discovery & Delivery
2 ONGOING RESEARCH PROJECTS
Nanotechnology: This involves using tiny particles to deliver drugs to specific cells or tissues. By targeting drug delivery, honed.life researchers aim to improve efficacy, reduce side effects, and enhance treatment outcomes.


what we stand for
Innovation, health, humanity.
"For decades, I've dedicated my career to researching the science behind aging and its impact on human health. honed.life's approach to personalized longevity plans is truly groundbreaking. Their focus on data-driven insights and cutting-edge interventions aligns perfectly with the future of healthcare. By empowering individuals with a proactive approach to optimizing their healthspan, honed.life will help people live longer, healthier lives. If you're serious about taking control of your longevity journey, honed.life is a valuable resource you can't afford to miss."
Megan Brown
CMO and Co-Founder of honed.life











